Your body will thank you.
Hand-selected raw materials, an FDA certified manufacturing facility, and state-of-the-art extraction are just some of the things that make Eables CBD unique.

Registered Industrial Hemp
All of our hemp comes from a network of US farms - each one having registered as a producer of industrial hemp in accordance with the 2018 farm bill classification.

Born in Colorado
Our state-of-the-art extraction facility is located in Colorado, and all of our raw materials are grown and processed in the United States.

All Natural
All of Eables CBD raw materials are tested at each one of our farms, before and after extraction. We also test all of our final products as well.

Raving Fans
Don't take it from us - just ask any of our customers what their experience is with Eables.
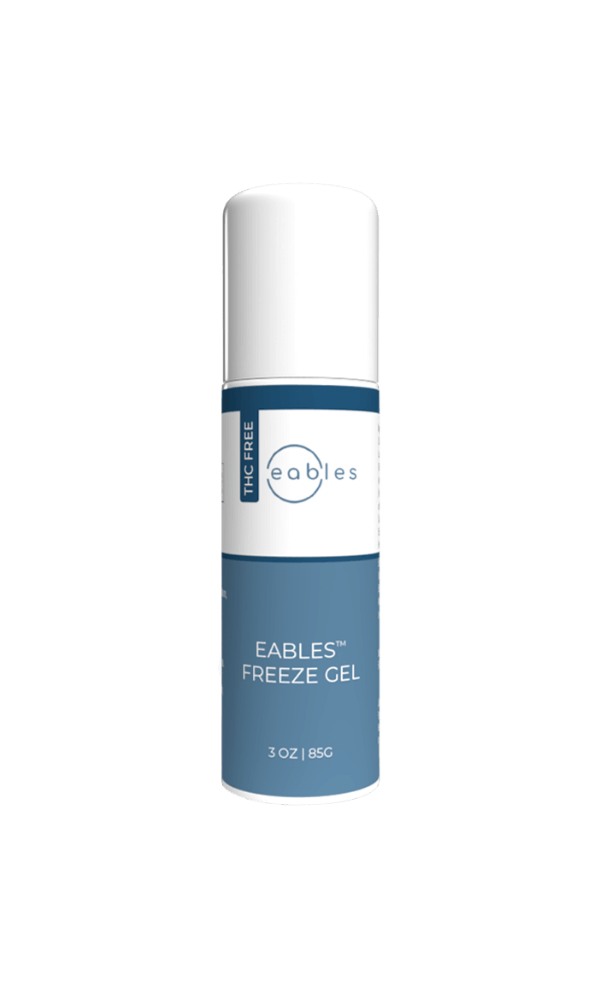
Natural Pain Relief
Discover the ice cold pain relief of Eables Freeze Gel. Specifically formulated with CBD, Menthol, Aloe, and camphor to target areas of intense pain.
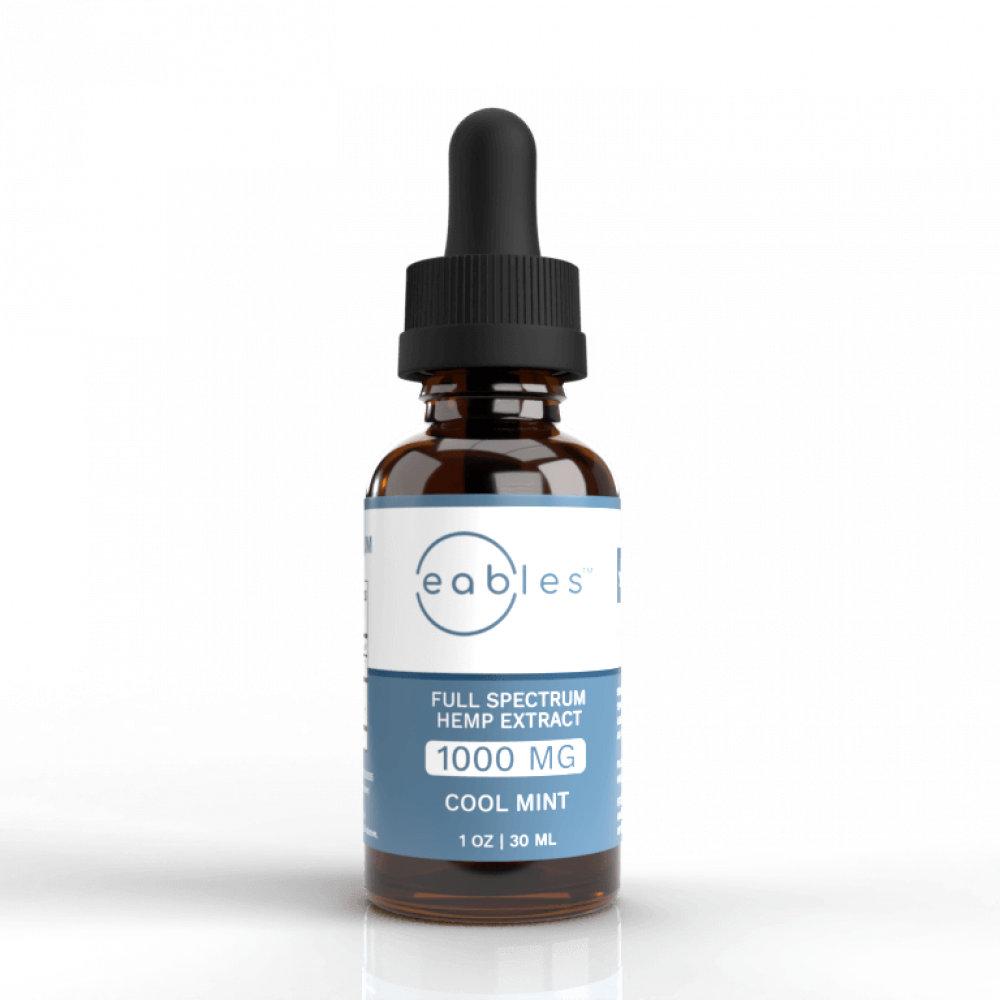
Eables CBD Oil
Natural hemp remedies to #FindYourCalm.
Full Spectrum CBD
Every part of the plant.
- <0.3% Δ9-THC
- CBDa, CBC, CBG, etc
- Organic Coconut (MCT) Oil
- Organic Food Grade Peppermint Oil
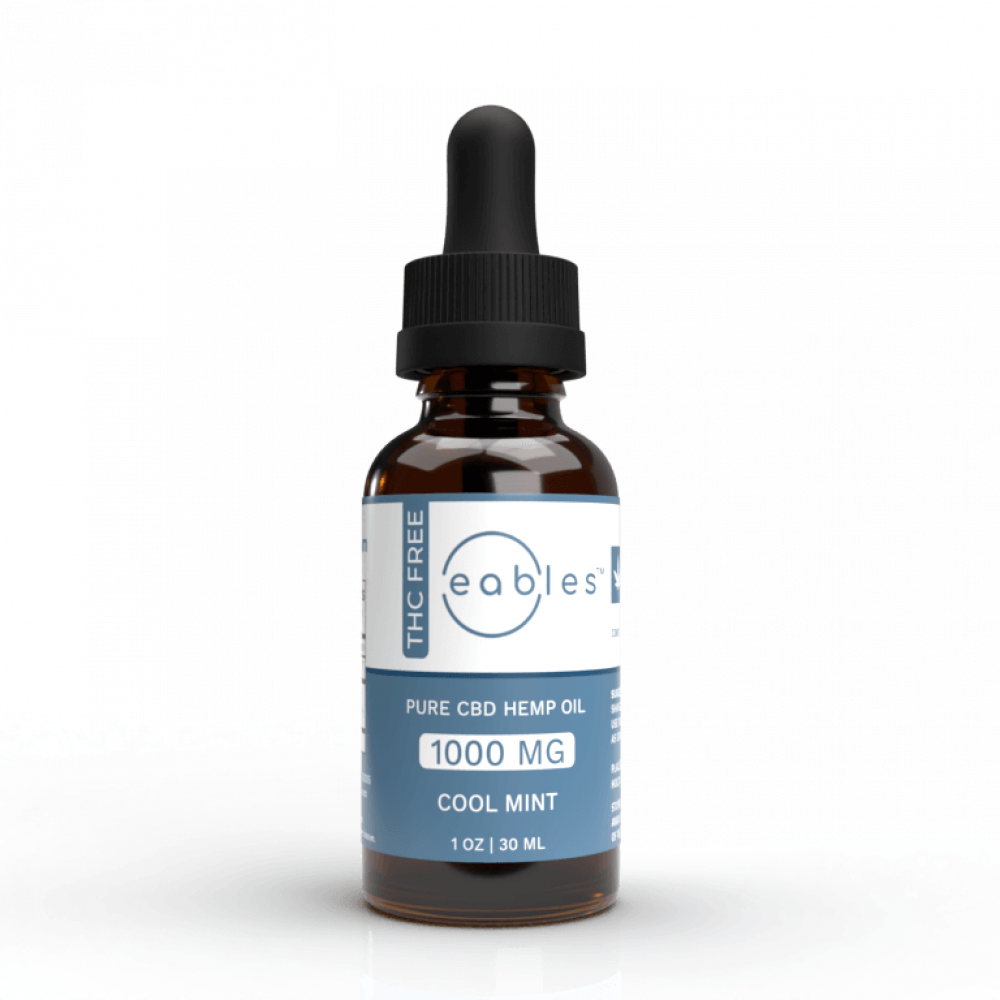
Pure CBD
Pharmaceutical-grade pure CBD only.
- THC FREE
- Pure CBD Isolate
- Organic Coconut (MCT) Oil
- Food Grade Peppermint Oil
Don't Take it From Us
Learn About CBD
If you prefer to talk to a human, that's fine too.
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty 



